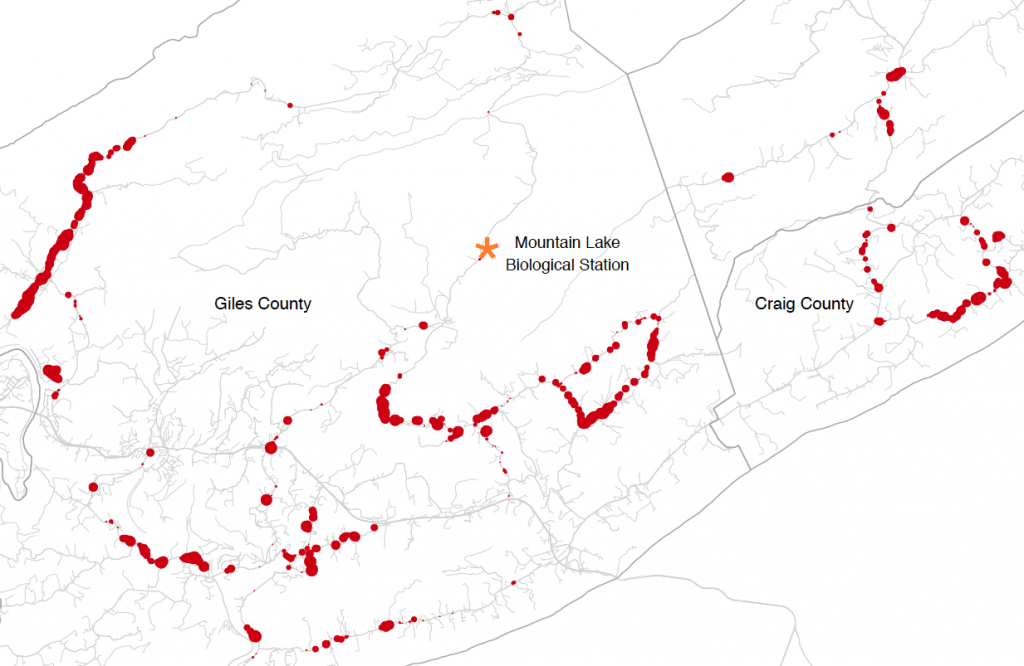
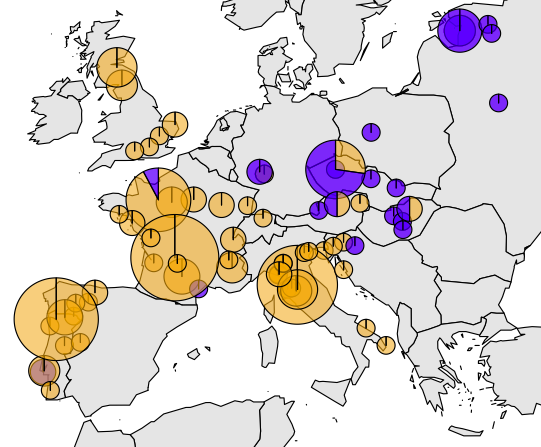
Populations can be genetically isolated by both geographic distance and by differences in their ecology or environment that decrease the rate of successful migration. Empirical studies often seek to investigate the relationship between genetic differentiation and some ecological variable(s) while accounting for geographic distance, but common approaches to this problem (such as the partial Mantel test) have a number of drawbacks. In this article, we present a Bayesian method that enables users to quantify the relative contributions of geographic distance and ecological distance to genetic differentiation between sampled populations or individuals. We model the allele frequencies in a set of populations at a set of unlinked loci as spatially correlated Gaussian processes, in which the covariance structure is a decreasing function of both geographic and ecological distance. Parameters of the model are estimated using a Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm. We call this method Bayesian Estimation of Differentiation in Alleles by Spatial Structure and Local Ecology (BEDASSLE), and have implemented it in a user-friendly format in the statistical platform R. We demonstrate its utility with a simulation study and empirical applications to human and teosinte datasets.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1302.3274
2013年6月27日星期四
2013年5月1日星期三
2013年4月30日星期二
Stamen maps with spplot
Stamen maps with spplot
Several R packages provide an interface to query map services (Google Maps,Stamen Maps or OpenStreetMap) to obtain raster images from them. As far as I know, there are three packages devoted to this task: RgoogleMaps,OpenStreetMap and ggmap. The latter two are increasingly popular with a wide collection of providers.
2013年4月23日星期二
2013年4月21日星期日
OpenStreetMap package of R - get beautiful maps
The bigest change in the new version is the addition of dozens of tile servers, giving the user the option of many different map looks, including those from Bing, MapQuest and Apple.
nm = c("osm", "maptoolkit-topo",
"waze", "mapquest", "mapquest-aerial",
"bing", "stamen-toner", "stamen-terrain",
"stamen-watercolor", "osm-german", "osm-wanderreitkarte",
"mapbox", "esri", "esri-topo",
"nps", "apple-iphoto", "skobbler",
"opencyclemap", "osm-transport",
"osm-public-transport", "osm-bbike", "osm-bbike-german")
png(width=1200,height=2200)
par(mfrow=c(6,4))
for(i in 1:length(nm)){
print(nm[i])
map = openmap(c(lat= 38.05025395161289, lon= -123.03314208984375),
c(lat= 36.36822190085111, lon= -120.69580078125),
minNumTiles=9,type=nm[i])
plot(map)
title(nm[i],cex.main=4)
}
dev.off()
http://blog.fellstat.com/?p=356
2013年3月28日星期四
2013年3月22日星期五
2013年3月20日星期三
A Geospatial Modelling Approach Integrating Archaeobotany and Genetics to Trace the Origin and Dispersal of Domesticated Plants
A Geospatial Modelling Approach Integrating Archaeobotany and Genetics to Trace the Origin and Dispersal of Domesticated Plants
Background
The study of the prehistoric origins and dispersal routes of domesticated plants is often based on the analysis of either archaeobotanical or genetic data. As more data become available, spatially explicit models of crop dispersal can be used to combine different types of evidence.
Methodology/Principal Findings
We present a model in which a crop disperses through a landscape that is represented by a conductance matrix. From this matrix, we derive least-cost distances from the geographical origin of the crop and use these to predict the age of archaeological crop remains and the heterozygosity of crop populations. We use measures of the overlap and divergence of dispersal trajectories to predict genetic similarity between crop populations. The conductance matrix is constructed from environmental variables using a number of parameters. Model parameters are determined with multiple-criteria optimization, simultaneously fitting the archaeobotanical and genetic data. The consilience reached by the model is the extent to which it converges around solutions optimal for both archaeobotanical and genetic data. We apply the modelling approach to the dispersal of maize in the Americas.
Conclusions/Significance
The approach makes possible the integrative inference of crop dispersal processes, while controlling model complexity and computational requirements.
van Etten J, Hijmans RJ (2010) A Geospatial Modelling Approach Integrating Archaeobotany and Genetics to Trace the Origin and Dispersal of Domesticated Plants. PLoS ONE 5(8): e12060. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012060
2012年9月8日星期六
2012年8月10日星期五
Map biodiversity records with rgbif and ggmap packages in R
Another example for geographic mapping in R
http://vijaybarve.wordpress.com/2012/07/23/map-biodiversity-records-with-rgbif-and-ggmap-packages-in-r/
http://vijaybarve.wordpress.com/2012/07/23/map-biodiversity-records-with-rgbif-and-ggmap-packages-in-r/
2012年8月8日星期三
Reclass ascii grid with awk
BEGIN {FS =" ";} {if (NR < 7)else {for (i =1;i <=NF ;i ++) {if ($i == "-9999")res =-9999;else if ($i <a )res =0;else res =1;printf "%s ",res ; }printf "\n "; } }
The script requires as a parameter a a threshold. Every value below this threshold is classified as 0 and every value above as 1. No data values (-9999) are not affected. Once the script is saved to reclass.awk, it can be calle with:
awk -v a =0.4 -f reclass .awk ingrid .asc >outgrid .asc
2012年7月20日星期五
2012年6月29日星期五
2012年6月28日星期四
chinese GIS data resources
Chinees GIS resources
Here is a list of useful Chinese GIS resources:
- CHGIS (download and CD)
- China Dimensions
- CloudMade (dowload)
- GRASS-Wiki
2012年6月4日星期一
2012年6月1日星期五
2012年4月27日星期五
2012年4月12日星期四
2012年3月22日星期四
订阅:
评论 (Atom)